The Table of Content


Family Research:









Available Help:



|
Government and Politics
Scotland's head of state is the monarch of the United Kingdom, currently Queen Elizabeth II (since 1952). The title Elizabeth II caused controversy around the time of the queen's coronation, as there had never been an Elizabeth I in Scotland. A legal case, MacCormick v. Lord Advocate (1953 SC 396), was taken to contest the right of the Queen to title herself Elizabeth II within Scotland, arguing that to do so would be a breach of Article 1 of the Treaty of Union.
The case was lost and it was decided that future British monarchs would be numbered according to either their English or Scottish predecessors, whichever number is higher. Hence, any future King James would be styled James VIII (since the last Scottish King James was James VII (also James II of England, etc.)) whilst the next King Henry would be King Henry IX throughout the UK despite the fact that there have been no Scottish kings of the name.
Scotland has partial self-government within the United Kingdom as well as representation in the UK Parliament. Executive and legislative powers have been devolved to, respectively, the Scottish Government and the Scottish Parliament at Holyrood in Edinburgh. The United Kingdom Parliament retains power over a set list of areas explicitly specified in the Scotland Act 1998 as reserved matters, including, for example, levels of UK taxes, social security, defense, international relations and broadcasting.
The Scottish Parliament has legislative authority for all other areas relating to Scotland, as well as limited power to vary income tax, a power it has yet to exercise. The Prime Minister, in a BBC Scotland interview, has indicated that the Scottish Parliament could be given more tax-raising powers.
The Scottish Parliament can give legislative consent over devolved matters back to Westminster by passing a Legislative Consent Motion if United Kingdom-wide legislation is considered to be more appropriate for a certain issue. The programs of legislation enacted by the Scottish Parliament have seen a divergence in the provision of public services compared to the rest of the United Kingdom. For instance, the costs of a university education, and care services for the elderly are free at point of use in Scotland, while fees are paid in the rest of the UK. Scotland was the first country in the UK to ban smoking in enclosed public places.
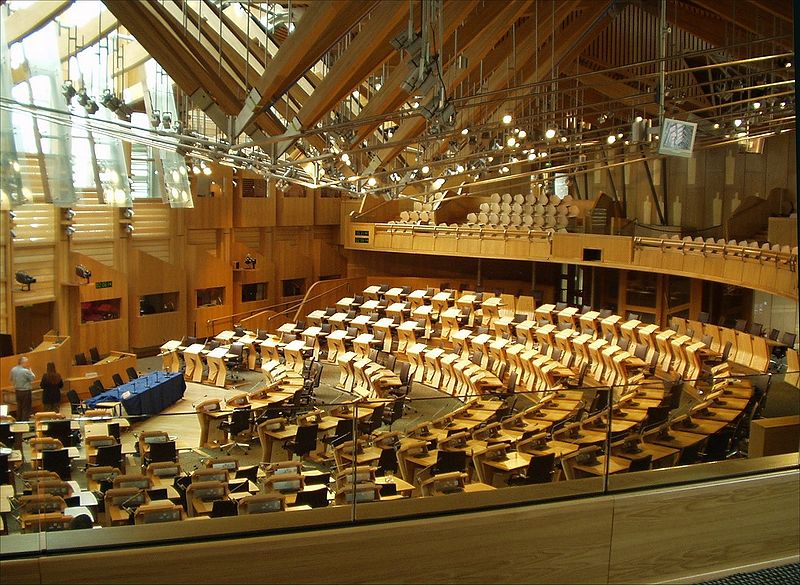

The debating chamber of
the Scottish Parliament Building
The Scottish Parliament is a unicameral legislature comprising 129 members, 73 of whom represent individual constituencies and are elected on a first past the post system; 56 are elected in eight different electoral regions by the additional member system, serving for a four year period. The Queen appoints one member of the Scottish Parliament, (MSP), on the nomination of the Parliament, to be First Minister. Other Ministers are also appointed by the Queen on the nomination of the Parliament and together with the First Minister they make up the Scottish Government, the executive arm of government.
In the 2007 election, the Scottish National Party (SNP), which campaigns for Scottish independence, won the election by a one seat majority. The leader of the SNP, Alex Salmond, was elected First Minister on 16 May 2007 as head of a minority government. The Labor Party became the largest opposition party, with the Conservative Party, the Liberal Democrats, and the Green Party are also represented in the Parliament. Margo MacDonald is the only independent MSP sitting in Parliament.
Scotland is represented in the British House of Commons by 59 MPs elected from territory-based Scottish constituencies. The Scotland Office represents the UK government in Scotland on reserved matters and represents Scottish interests within the UK government. The Scotland office is led by the Secretary of State for Scotland, who sits in the Cabinet of the United Kingdom, the current incumbent being Jim Murphy.
Administrative Subdivisions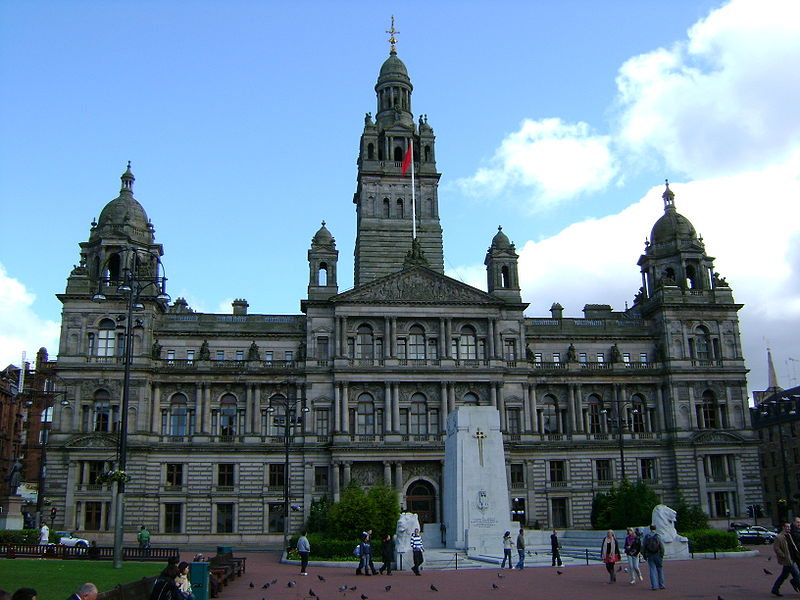 
Glasgow City Chambers viewed
from George Square
Historical types subdivisions of Scotland include the mormaerdom, stewartry, earldom, burgh, parish, county and regions and districts. The names of these areas are still sometimes used as geographical descriptors.
Modern Scotland is subdivided in various ways depending on the purpose. For local government, there have been 32 council areas since 1996, whose councils are unitary authorities responsible for the provision of all local government services. Community councils are informal organisations that represent specific sub-divisions of a council area.
For the Parliament of the United Kingdom, there are 59 constituencies. The Scottish fire brigades and police forces are still based on the system of regions introduced in 1975. For healthcare and postal districts, and a number of other governmental and non-governmental organisations such as the churches, there are other long-standing methods of subdividing Scotland for the purposes of administration.
City status in the United Kingdom is determined by letters patent. There are six cities in Scotland: Aberdeen, Dundee, Edinburgh, Glasgow, most recently Inverness, and Stirling.
Scotland within the UK
A policy of devolution had been advocated by the three main UK parties with varying enthusiasm during recent history. The late Labor leader John Smith described the revival of a Scottish parliament as the "settled will of the Scottish people". The constitutional status of Scotland is nonetheless subject to ongoing debate. In 2007, the Scottish Government established a "National Conversation" on constitutional issues, proposing a number of options such as increasing the powers of the Scottish Parliament, federalism, or a referendum on Scottish independence from the United Kingdom. In rejecting the last option, the three main opposition parties in the Scottish Parliament have proposed a separate Scottish Constitutional Commission to investigate the distribution of powers between devolved Scottish and UK-wide bodies. In August 2009 the SNP proposed a Referendum Bill in order to hold a referendum on independence planned for November 2010, although because of immediate opposition from all other major parties, it was expected to be defeated.
Law and Criminal Justice
Scots law has a basis derived from Roman law, combining features of both uncodified civil law, dating back to the Corpus Juris Civilis, and common law with medieval sources.
The terms of the Treaty of Union with England in 1707 guaranteed the continued existence of a separate legal system in Scotland from that of England and Wales. Prior to 1611, there were several regional law systems in Scotland, most notably Udal law in Orkney and Shetland, based on old Norse law. Various other systems derived from common Celtic or Brehon laws survived in the Highlands until the 1800s.
Scots law provides for three types of courts responsible for the administration of justice: civil, criminal and heraldic. The supreme civil court is the Court of Session, although civil appeals can be taken to the Supreme Court of the United Kingdom (or before 1 Oct 2009, the House of Lords). The High Court of Justiciary is the supreme criminal court in Scotland. The Court of Session is housed at Parliament House, in Edinburgh, which was the home of the pre-Union Parliament of Scotland with the High Court of Justiciary and the Supreme Court of Appeal currently located at Lawnmarket. The sheriff court is the main criminal and civil court, hearing most of the cases. There are 49 sheriff courts throughout the country. District courts were introduced in 1975 for minor offences and small claims. The Court of the Lord Lyon regulates heraldry.
For many decades the Scots legal system was unique for a period in being the only legal system without a parliament. This ended with the advent of the Scottish Parliament which legislates for Scotland. Many features within the system have been preserved. Within criminal law, the Scots legal system is unique in having three possible verdicts: "guilty", "not guilty" and "not proven". Both "not guilty" and "not proven" result in an acquittal with no possibility of retrial. Many laws differ between Scotland and the rest of Britain, whereas many terms differ. Manslaughter, in England and Wales, becomes culpable homicide in Scotland, and arson becomes willful fire-raising. Procedure also differs. Scots juries consist of fifteen, not twelve jurors as is more common in English-speaking countries.
The civil legal system has however attracted much recent criticism from a senior Scottish Judge who referred to it as being "Victorian" and antiquated.
The Scottish Prison Service (SPS) manages the prisons in Scotland which contain between them over 8,500 prisoners. The Cabinet Secretary for Justice is responsible for the Scottish Prison Service within the Scottish Government.
Geography and Natural History
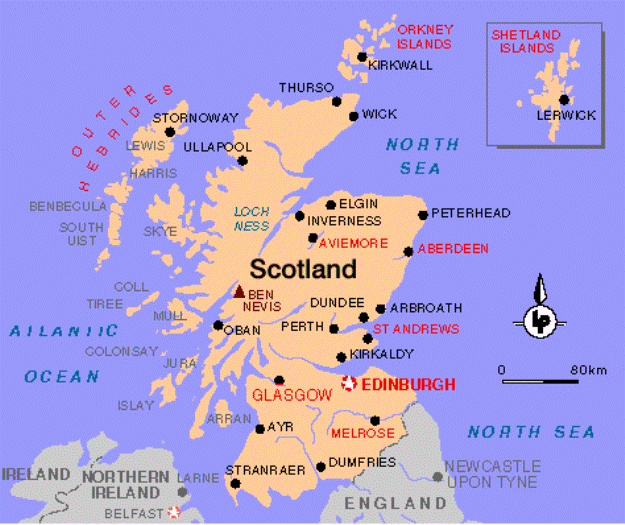
The main land of Scotland comprises the northern third of the land mass of the island of Great Britain, which lies off the northwest coast of Continental Europe. The total area is 78,772 km2 (30,414 sq mi), comparable to the size of the Czech Republic, making Scotland the 117th largest country in the world. Scotland's only land border is with England, and runs for 96 kilometres (60 mi) between the basin of the River Tweed on the east coast and the Solway Firth in the west. The Atlantic Ocean borders the west coast and the North Sea is to the east. The island of Ireland lies only 30 kilometres (19 mi) from the southwestern peninsula of Kintyre; Norway is 305 kilometres (190 mi) to the east and the Faroes, 270 kilometres (168 mi) to the north.
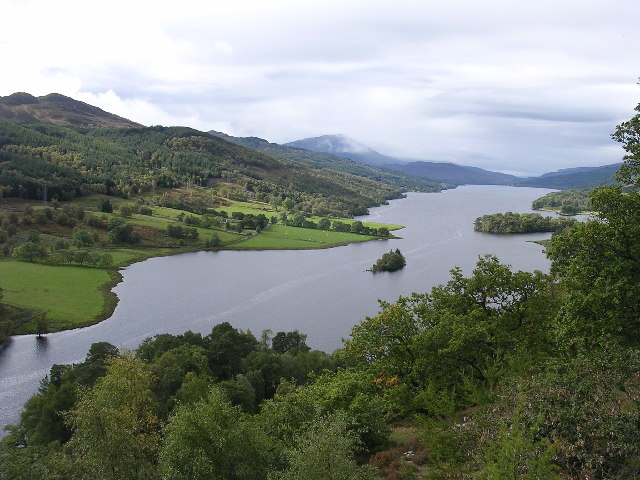

Loch Tummel in Perth and Kinross.
The territorial extent of Scotland is generally that established by the 1237 Treaty of York between Scotland and Kingdom of England and the 1266 Treaty of Perth between Scotland and Norway. Important exceptions include the Isle of Man, which having been lost to England in the 14th century is now a crown dependency outside of the United Kingdom; the island groups Orkney and Shetland, which were acquired from Norway in 1472; and Berwick-upon-Tweed, lost to England in 1482.
The geographical center of Scotland lies a few miles from the village of Newtonmore in Badenoch. Rising to 1,344 metres (4,409 ft) above sea level, Scotland's highest point is the summit of Ben Nevis, in Lochaber, while Scotland's longest river, the River Tay, flows for a distance of 190 kilometres (118 mi).
Geology and Geomorphology
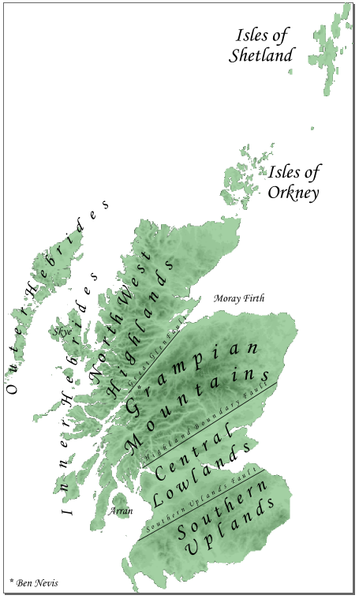
The whole of Scotland was covered by ice sheets during the Pleistocene ice ages and the landscape is much affected by glaciations. From a geological perspective the country has three main sub-divisions.
Relief map of Scotland
Highlands and Islands
The Highlands and Islands lie to the north and west of the Highland Boundary Fault, which runs from Arran to Stonehaven. This part of Scotland largely comprises ancient rocks from the Cambrian and Precambrian which were uplifted during the later Caledonian Orogeny. It is interspersed with igneous intrusions of a more recent age, the remnants of which have formed mountain massifs such as the Cairngorms and Skye Cuillins.
A significant exception to the above are the fossil-bearing beds of Old Red Sandstones found principally along the Moray Firth coast. The Highlands are generally mountainous and the highest elevations in the British Isles are found here. Scotland has over 790 islands, divided into four main groups: Shetland, Orkney, and the Inner Hebrides and Outer Hebrides. There are numerous bodies of freshwater including Loch Lomond and Loch Ness. Some parts of the coastline consist of machair, a low lying dune pasture land.
Central Lowlands
The Central Lowlands is a rift valley mainly comprising Paleozoic formations. Many of these sediments have economic significance for it is here that the coal and iron bearing rocks that fuelled Scotland's industrial revolution are to be found. This area has also experienced intense volcanism, Arthur’s Seat in Edinburgh being the remnant of a once much larger volcano. This area is relatively low-lying, although even here hills such as the Ochils and Campsie Fells are rarely far from view.
Southern Uplands
The Southern Uplands are a range of hills almost 200 kilometres (124 mi) long, interspersed with broad valleys. They lie south of a second fault line (the Southern Uplands fault) that runs from Girvan to Dunbar. The geological foundations largely comprise Silurian deposits laid down some 4–500 million years ago. The high point of the Southern Uplands is Merrick with an elevation of 843 m (2,766 ft). The Southern Uplands is home to the UK's highest village, Wanlockhead (430 m/1,411 ft above sea level).
Climate
The climate of Scotland is temperate and oceanic, and tends to be very changeable. It is warmed by the Gulf Stream from the Atlantic, and as such has much milder winters (but cooler, wetter summers) than areas on similar latitudes, for example Labrador, Canada, Moscow, or the Kamchatka Peninsula on the opposite side of Eurasia. However, temperatures are generally lower than in the rest of the UK, with the coldest ever UK temperature of −16.96 °F recorded at Braemar in the Grampian Mountains, on 11 February 1895. Winter maximums average 42.8 °F in the lowlands, with summer maximums averaging 64.4 °F. The highest temperature recorded was 91.22 °F at Greycrook, Scottish Borders on 9 August 2003.

Tiree, one of the sunniest locations
in Scotland.
In general, the west of Scotland is usually warmer than the east, owing to the influence of Atlantic ocean currents and the colder surface temperatures of the North Sea. Tiree, in the Inner Hebrides, is one of the sunniest places in the country: it had 300 days of sunshine in 1975. Rainfall varies widely across Scotland. The western highlands of Scotland are the wettest place, with annual rainfall exceeding 118.1 in. In comparison, much of lowland Scotland receives less than 31.5 in annually. Heavy snowfall is not common in the lowlands, but becomes more common with altitude. Braemar experiences an average of 59 snow days per year, while coastal areas have an average of fewer than 10 days.
Flora and Fauna
Scotland's wildlife is typical of the north west of Europe, although several of the larger mammals such as the Lynx, Brown Bear, Wolf, Elk and Walrus were hunted to extinction in historic times. There are important populations of seals and internationally significant nesting grounds for a variety of seabirds such as Gannets. The Golden Eagle is something of a national icon.

Twinflower

Mountain Hare
On the high mountain tops species including Ptarmigan, Mountain Hare and Stoat can be seen in their white color phase during winter months. Remnants of the native Scots Pine forest exist and within these areas the Scottish Crossbill, Britain's only endemic bird, can be found alongside Capercaillie, Wildcat, Red Squirrel and Pine Marten. In recent years various animals have been re-introduced, including the White-tailed Sea Eagle in 1975, the Red Kite in the 1980s, and more recently there have been experimental projects involving the Beaver and Wild Boar.
The flora of the country is varied incorporating both deciduous and coniferous woodland and moorland and tundra species. However, large scale commercial tree planting and the management of upland moorland habitat for the grazing of sheep and commercial field sport activities impacts upon the distribution of indigenous plants and animals. The UK's tallest tree is the Stronardron Douglas Fir located in Argyll, and the Fortingall Yew may be 5,000 years old and is probably the oldest living thing in Europe. Although the number of native vascular plants is low by world standards, Scotland's substantial bryophyte flora is of global importance.
Economy and infrastructure
Scotland has a western style open mixed economy which is closely linked with that of the rest of Europe and the wider world. Traditionally, the Scottish economy has been dominated by heavy industry underpinned by the shipbuilding in Glasgow, coal mining and steel industries. Petroleum related industries associated with the extraction of North Sea oil have also been important employers from the 1970s, especially in the north east of Scotland.
De-industrialization during the 1970s and 1980s saw a shift from a manufacturing focus towards a more service oriented economy. Edinburgh is the financial services centre of Scotland and the sixth largest financial centre in Europe in terms of funds under management, behind London, Paris, Frankfurt, Zurich and Amsterdam, with many large finance firms based there, including: Lloyds Banking Group (owners of the Halifax Bank of Scotland); the Government owned Royal Bank of Scotland and Standard Life.
In 2005, total Scottish exports (excluding intra-UK trade) were provisionally estimated to be £17.5 billion, of which 70% (£12.2 billion) were attributable to manufacturing. Scotland's primary exports include whisky, electronics and financial services. The United States, Netherlands, Germany, France and Spain constitute the country's major export markets. In 2006, the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of Scotland (excluding oil and gas production from 'Scottish' waters) was just over £86 billion, giving a per capita GDP of £16,900.
Tourism is widely recognized as a key contributor to the Scottish economy. A briefing published in 2002 by the Scottish Parliament Information Centre, (SPICe), for the Scottish Parliament's Enterprise and Life Long Learning Committee, stated that tourism accounted for up to 5% of GDP and 7.5% of employment.
As of May 2009 the unemployment rate in Scotland stood at 6.6%— slightly lower than the UK average and lower than that of the majority of EU countries.
The most recent government figures (for 2006/7) suggest that Scotland would be in budget surplus to the tune of more than £800m if it received its geographical share of North Sea revenues. The net fiscal balance, which is the budget balance plus capital investment, reported a deficit of £2.7 billion (2.1% of GDP) including Scotland's full geographical share of North Sea revenue, or a £10.2bn deficit if the North Sea share is excluded.
Currency
Although the Bank of England is the central bank for the UK, three Scottish clearing banks still issue their own Sterling banknotes: the Bank of Scotland; the Royal Bank of Scotland; and the Clydesdale Bank. The current value of the Scottish banknotes in circulation is £1.5 billion.
Transportation
Scotland has five main international airports (Glasgow International, Edinburgh, Aberdeen, Glasgow Prestwick and Inverness) which together serve 150 international destinations with a wide variety of scheduled and chartered flights. BAA operates three airports, (Aberdeen, Edinburgh and Glasgow International), and Highland and Islands Airports operates 11 regional airports, (including Inverness), which serve the more remote locations of Scotland. Infratil operates Glasgow Prestwick.
The Scottish motorways and major trunk roads are managed by Transport Scotland. The rest of the road network is managed by the Scottish local authorities in each of their areas.
Regular ferry services operate between the Scottish mainland and island communities. These services are mostly run by Caledonian MacBrayne, but some are operated by local councils. Other ferry routes, served by multiple companies, connect to Northern Ireland, Belgium, Norway, the Faroe Islands and also Iceland.
Network Rail Infrastructure Limited owns and operates the fixed infrastructure assets of the railway system in Scotland, while the Scottish Government maintains overall responsibility for rail strategy and funding in Scotland. Scotland’s rail network has around 340 railway stations and 3,000 kilometres of track with over 62 million passenger journeys made each year.
Scotland's rail network is managed by Transport Scotland. The East Coast and West Coast Main Railway lines and the Cross Country Line connect the major cities and towns of Scotland with each other and with the rail network in England. Domestic rail services within Scotland are operated by First ScotRail. Furthermore in Glasgow there is a small integrated subway system which has been in existence since 1896. There are currently 15 stations and there is a daily ridership of just under 40,000. There are plans to extend the subway system in time for the 2014 Commonwealth Games.
The East Coast Main Line includes that section of the network which crosses the Firth of Forth via the Forth Bridge. Completed in 1890, this cantilever bridge has been described as "the one internationally recognized Scottish landmark".
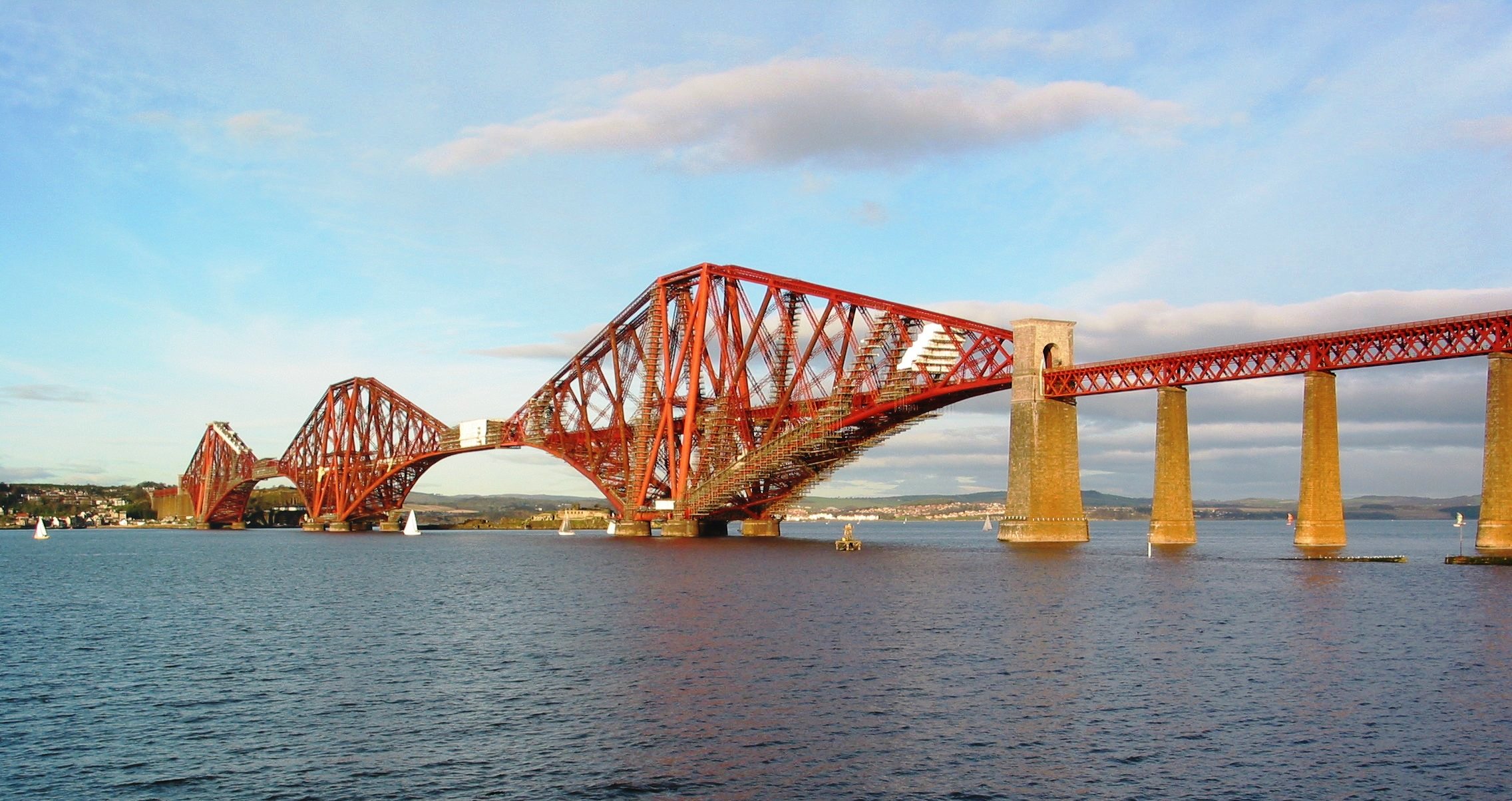

Forth Bridge
Demography
The population of Scotland in the 2001 census was 5,062,011. This has risen to 5,168,500 according to June 2008 estimates. This would make Scotland the 112th largest country by population if it were a sovereign state. Although Edinburgh is the capital of Scotland it is not the largest city. With a population of just over 584,000 this honour falls to Glasgow. Indeed, the Greater Glasgow conurbation, with a population of almost 1.2 million, is home to nearly a quarter of Scotland's population.
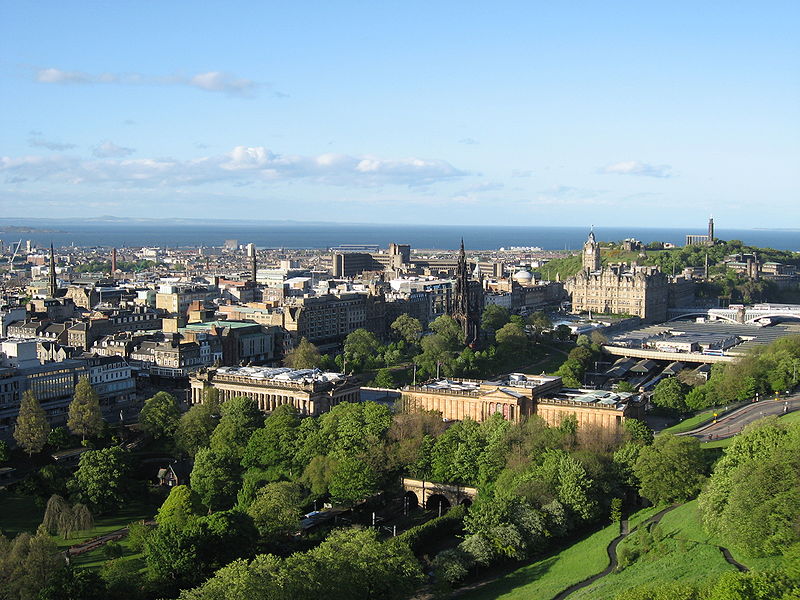

Edinburgh, from the castle.
The Central Belt is where most of the main towns and cities are located. Glasgow is to the west, while Edinburgh and Dundee lie on the east coast. Scotland's only major city outside the Central Belt is Aberdeen, on the east coast to the north. The Highlands are sparsely populated, although the city of Inverness has experienced rapid growth in recent years.
In general only the more accessible and larger islands retain human populations, and fewer than 90 are currently inhabited. The Southern Uplands are essentially rural in nature and dominated by agriculture and forestry. Because of housing problems in Glasgow and Edinburgh, five new towns were created between 1947 and 1966. They are East Kilbride, Glenrothes, Livingston, Cumbernauld, and Irvine.
Because of immigration since World War II, Glasgow, Edinburgh and Dundee have small South Asian communities. Since the recent Enlargement of the European Union there has been an increased number of people from Central and Eastern Europe moving to Scotland, and it is estimated that between 40,000 and 50,000 Poles are now living in the country. As of 2001, there are 16,310 ethnic Chinese resident in Scotland. The ethnic groups within Scotland are as follows: White, 97.99%; South Asian, 1.09%; Black, 0.16%; Mixed, 0.25%; Chinese, 0.32% and Other, 0.19%.
Map of Scottish clans
Scotland has three officially recognized languages: English, Scots and Scottish Gaelic. Almost all Scots speak Scottish Standard English, and in 1996 the General Register Office for Scotland estimated that 30% of the population are fluent in Scots. Gaelic is mostly spoken in the Western Isles, where a large number of people still speak it; however, nationally its use is confined to just 1% of the population. The number of Gaelic speakers in Scotland dropped from 250,000 – 7% of the population – in 1881 to 60,000 today.
There are many more people with Scottish ancestry living abroad than the total population of Scotland. In the 2000 Census, 9.2 million Americans self-reported some kind of Scottish descent. Ulster's Protestant population is mainly of lowland Scottish descent, and it is estimated that there are more than 27 million descendants of the Scots-Irish migration now living in the U.S. In Canada, the Scottish-Canadian community accounts for 4.7 million people. About 20% of the original European settler population of New Zealand came from Scotland.
Education and Religion
The Scottish education system has always remained distinct from education in the rest of United Kingdom, with a characteristic emphasis on a broad education. Scotland was the first country since Sparta in classical Greece to implement a system of general public education. Schooling was made compulsory for the first time in Scotland with the Education Act of 1496, then, in 1561, the Church of Scotland set out a national program for spiritual reform, including a school in every parish. Education continued to be a matter for the church rather than the state until the Education Act (1872).
The "Curriculum for Excellence" provides the curricular framework for children and young people from age 3 to 18. All 3- and 4-year-old children in Scotland are entitled to a free nursery place. Formal primary education begins at approximately 5 years old and lasts for 7 years (P1–P7); Today, children in Scotland sit Standard Grade, or more recently Intermediate exams at approximately 15 or 16. The school leaving age is 16, after which students may choose to remain at school and study for Access, Intermediate or Higher Grade and Advanced Higher exams. A small number of students at certain private, independent schools may follow the English system and study towards GCSEs and A and AS-Levels instead.
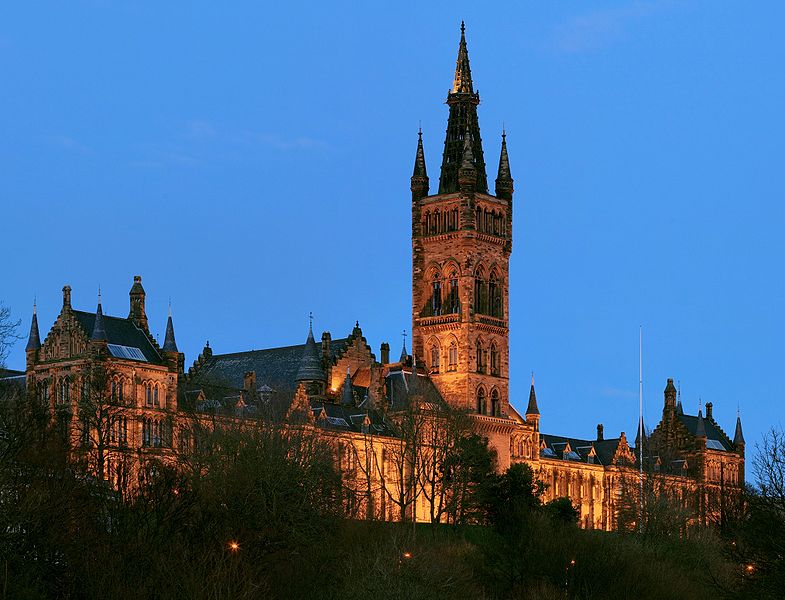

Gilbert Scott Building,
University of Glasgow
There are 14 Scottish universities, some of which are amongst the oldest in the world. These include the University of St Andrews, the University of Glasgow, the University of Edinburgh, the University of Aberdeen and the University of Dundee - many of which are ranked amongst the best in the UK. The country produces 1% of the world's published research with less than 0.1% of the world's population, and higher education institutions account for nine per cent of Scotland's service sector exports.
Religion

Iona Abbey, an early center
of Scottish Christianity.
Just over two-thirds (67%) of the Scottish population reported having a religion in 2001 with Christianity representing all but 2% of these. 28% of the population reported having no religious adherence.
Since the Scottish Reformation of 1560, the national Church of Scotland, (also known as The Kirk) has been Protestant and Reformed in theology. Since 1689 it has had a Presbyterian system of church government, and enjoys independence from the state. About 12% of the population are currently members of the Church of Scotland, with 40% claiming affinity. The Church operates a territorial parish structure, with every community in Scotland having a local congregation. Scotland also has a significant Roman Catholic population, 17% claiming that faith, particularly in the west.
After the Reformation, Roman Catholicism continued in the Highlands and some western islands like Uist and Barra, and was strengthened, during the 19th century by immigration from Ireland. Other Christian denominations in Scotland include the Free Church of Scotland, various other Presbyterian offshoots, and the Scottish Episcopal Church.
Islam is the largest non-Christian religion (estimated at around 40,000, which is less than 0.9% of the population), and there are also significant Jewish, Hindu and Sikh communities, especially in Glasgow. The Samyé Ling monastery near Eskdalemuir, which celebrated its 40th anniversary in 2007, includes the largest Buddhist temple in western Europe. In Scotland 14,052 people stated that Judaism was their current religion (14,014 "Jedi", 24 "Jedi Other" and 14 "Sith") and 2,733 stated that it was their religion of upbringing (2,682 "Jedi", 36 "Jedi Order" and 15 "Sith"). The proportion of people stating their religion as Jedi in Scotland was lower than that in England and Wales, at 0.277%. In April 2009, it emerged that eight police officers serving with Scotland's largest police force in Strathclyde listed their official religion as Jedi in voluntary diversity forms. The details were obtained in a Freedom of Information request by Jane's Police Review.
Healthcare
Healthcare in Scotland is mainly provided by NHS Scotland, Scotland's public healthcare system. The service was founded by the National Health Service (Scotland) Act 1947 (later repealed by the National Health Service (Scotland) Act 1978) that took effect on 5 July 1948 to coincide with the launch of the NHS in England and Wales. However, even prior to 1948, half of Scotland's landmass was already covered by state funded healthcare, provided by the Highlands and Islands Medical Service.
As at September 2009, NHS Scotland employed 168,976 staff including 68,681 nurses and midwives. In addition, there were also 16,256 medical staff (including GP's), 5,002 dental staff (including dental support) and 11,777 allied health profession staff. The Cabinet Secretary for Health and Wellbeing is responsible to the Scottish Parliament for the work of NHS Scotland.
Military
Although Scotland has a long military tradition that predates the Treaty of Union with England, its armed forces now form part of the British Armed Forces, with the notable exception of the Atholl Highlanders, Europe's only legal private army. In 2006, the infantry regiments of the Scottish Division were amalgamated to form the Royal Regiment of Scotland. Other distinctively Scottish regiments in the British Army include the Scots Guards, the Royal Scots Dragoon Guards and the Scottish Transport Regiment, a Territorial Army Regiment of the Royal Logistic Corps.
Because of their topography and perceived remoteness, parts of Scotland have housed many sensitive defense establishments, with mixed public feelings. Between 1960 and 1991, the Holy Loch was a base for the U.S. fleet of Polaris ballistic missile submarines. Today, Her Majesty's Naval Base Clyde, 25 miles (40 km) west of Glasgow, is the base for the four Trident-armed Vanguard class ballistic missile submarines that comprise the UK's nuclear deterrent. Scapa Flow was the major Fleet base for the Royal Navy until 1956.
Three frontline Royal Air Force bases are also located in Scotland. These are RAF Leuchars, RAF Kinloss and RAF Lossiemouth, the last of which is the most northerly air defense fighter base in the United Kingdom.
The only open-air live depleted uranium weapons test range in the British Isles is located near Dundrennan. As a result, over 7,000 radioactive munitions lie on the seabed of the Solway Firth.
Culture
Scottish music is a significant aspect of the nation's culture, with both traditional and modern influences. A famous traditional Scottish instrument is the Great Highland Bagpipe, a wind instrument consisting of three drones and a melody pipe (called the chanter), which are fed continuously by a reservoir of air in a bag. Bagpipe bands, featuring bagpipes and various types of drums, and showcasing Scottish music styles while creating new ones, have spread throughout the world. The clàrsach (harp), fiddle and accordion are also traditional Scottish instruments, the latter two heavily featured in Scottish country dance bands. Today, there are many successful Scottish bands and individual artists in varying styles.

A piper playing the Great Highland Bagpipe.
Scottish literature includes text written in English, Scottish Gaelic, Scots, French, and Latin. The poet and songwriter Robert Burns wrote in the Scots language, although much of his writing is also in English and in a "light" Scots dialect which is more accessible to a wider audience. Similarly, the writings of Sir Walter Scott and Sir Arthur Conan Doyle were internationally successful during the 19th and early 20th Centuries.
J. M. Barrie introduced the movement known as the " Kailyard school" at the end of the 19th century, which brought elements of fantasy and folklore back into fashion. This tradition has been viewed as a major stumbling block for Scottish literature, as it focused on an idealized, pastoral picture of Scottish culture. Some modern novelists, such as Irvine Welsh (of Train spotting fame), write in a distinctly Scottish English that reflects the harsher realities of contemporary life. More recently, author J.K. Rowling has become one of the most popular authors in the world (and one of the wealthiest) through her Harry Potter series, which she began writing from a coffee-shop in Edinburgh.
Scottish theatre has for many years played an important role in Scottish society, from the music hall variety of Sir Harry Lauder and his contemporaries to the more serious plays put on at the Citizens Theatre in Glasgow and many other theatres throughout Scotland.
The national broadcaster is BBC Scotland (BBC Alba in Gaelic), a constituent part of the British Broadcasting Corporation, the publicly funded broadcaster of the United Kingdom. It runs two national television stations and the national radio stations, BBC Radio Scotland and BBC Radio nan Gaidheal, amongst others. The main Scottish commercial television station is STV. National newspapers such as the Daily Record, The Herald, and The Scotsman are all produced in Scotland. Important regional dailies include the Evening News in Edinburgh 'The Courier in Dundee in the east, and The Press and Journal serving Aberdeen and the north. Scotland is represented at the Celtic Media Festival, which showcases film and television from the Celtic countries. Scottish entrants have won many awards since the festival began in 1980.
As one of the Celtic nations, Scotland and Scottish culture is represented at inter-Celtic events at home and over the world. Scotland hosts several music festivals including Celtic Connections (Glasgow), and the Hebridean Celtic Festival (Stornoway). Festivals celebrating Celtic culture, such as Festival Inter-celtique de Lorient (Brittany), the Pan Celtic Festival (Ireland), and the National Celtic Festival (Portarlington, Australia), feature elements of Scottish culture such as language, music and dance.
Sports
Sport is an important element in Scottish culture, with the country hosting many of its own national sporting competitions. It enjoys independent representation at many international sporting events including the FIFA World Cup, the Rugby Union World Cup, the Rugby League World Cup, the Cricket World Cup and the Commonwealth Games, but not at the Olympic Games where Scottish athletes are part of the Great Britain team. Scotland has its own national governing bodies, such as the Scottish Football Association (the second oldest national football association in the world) and the Scottish Rugby Union. Variations of football have been played in Scotland for centuries with the earliest reference dating back to 1424. Association football is now the national sport and the Scottish Cup is the world's oldest national trophy.
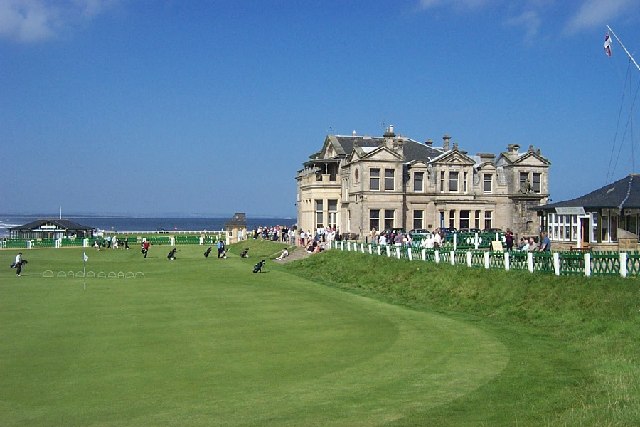

Old Course at St Andrews-18th Hole and Club House
Scotland (and England) fielded the first international football team. Scottish clubs have been successful in European competitions with Celtic winning the European Cup in 1967, Rangers and Aberdeen winning the UEFA Cup Winners' Cup in 1972 and 1983 respectively, and Aberdeen also winning the UEFA Super Cup in 1983. The Fife town of St. Andrews is known internationally as the Home of Golf and to many golfers the Old Course, an ancient links course dating to before 1574, is considered to be a site of pilgrimage. There are many other famous golf courses in Scotland, including Carnoustie, Gleneagles, Muirfield and Royal Troon. Other distinctive features of the national sporting culture include the Highland games, curling and shinty. Scotland played host to the Commonwealth Games in 1970 and 1986, and will do so again in 2014.
National Symbols
The national flag of Scotland, known as the Saltire or St. Andrew's Cross, dates (at least in legend) from the 9th century, and is thus the oldest national flag still in use. Since 1606 the Saltire has also formed part of the design of the Union Flag. There are numerous other symbols and symbolic artifacts, both official and unofficial, including the thistle, the nation's floral emblem, the 6 April 1320 statement of political independence the Declaration of Arbroath, the textile pattern tartan that often signifies a particular Scottish clan, and the Lion Rampant flag.
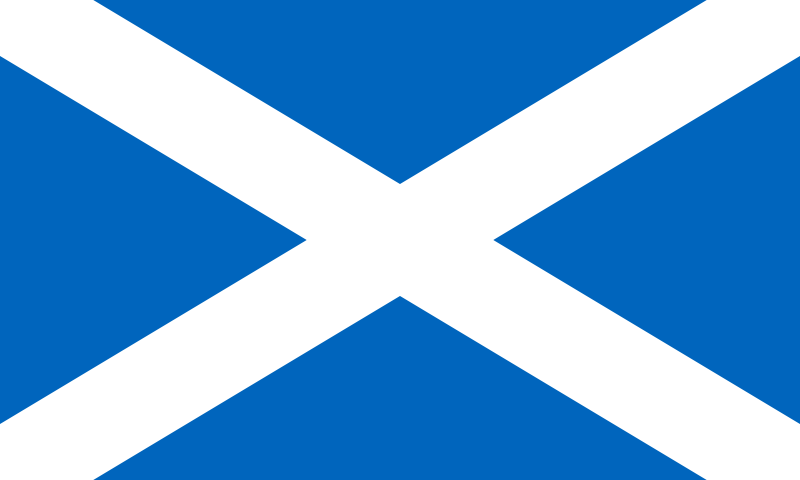

The Flag of Scotland
Flower of Scotland is popularly held to be the National Anthem of Scotland, and is played at events such as football or rugby matches involving the Scotland national team. Scotland the Brave is used for the Scottish team at the Commonwealth Games. However, since devolution, more serious discussion of the issue has led to the use of Flower of Scotland being disputed. Other candidates include Highland Cathedral, Scots Wha Hae and A Man's A Man for A' That.
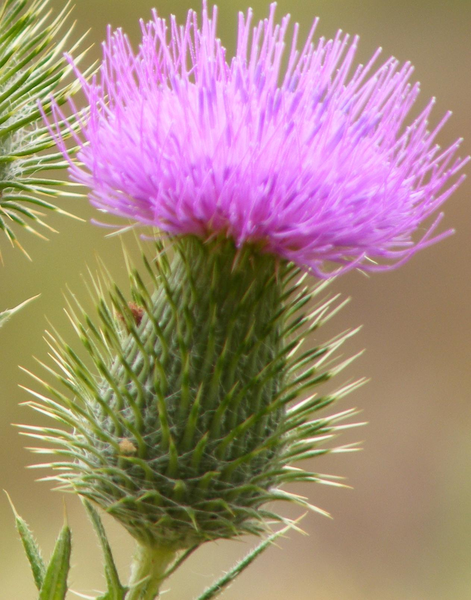

The "thistle" Scotland's floral emblem.
St Andrew's Day, 30 November, is the national day, although Burns' Night tends to be more widely observed. Tartan Day is a recent innovation from Canada. In 2006, the Scottish Parliament passed the St. Andrew's Day Bank Holiday (Scotland) Act 2007, designating the day to be an official bank holiday.
  
|




















